নকল হইতে সাবধান! প্রোডাক্ট রিসিভ করার সময় অবশ্যই মাশরুম কেয়ারের লোগো সম্বলিত QR CODE স্ক্যান করে নিবেন।
আজকের জন্য স্পেশাল অফার
ভয় নয়, জয় করুন। ডা-য়া-বেটিস থেকে স্থায়ী মুক্তি নিন।
ডাঃ হাবীব স্যারের যুগান্তকারী আবিষ্কার বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর যা মাত্র ৬-৭ মাসের মধ্যে শরীর থেকে ডায়া/বেটিস সম্পূর্ণরুপে বিদায় করতে স-ক্ষম।





বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর- এখন অভিজ্ঞ ডাক্তারদের দ্বারা সু-পারিশকৃত!
১টি বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটরের মূল্য
রেগুলার মূল্য ১২০০ টাকা
অফার মূল্য মাত্র ৮৫০ টাকা
২টি বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটরের মূল্য
রেগুলার মূল্য ২৪০০ টাকা
অফার মূল্য মাত্র ১৪৯৯ টাকা
৩টি বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটরের মূল্য
রেগুলার মূল্য ৩৬০০ টাকা
অফার মূল্য মাত্র ২১৯৯ টাকা
১ পিসের বেশি অর্ডার করলে সারা বাংলাদেশ ডেলিভারি চার্জ একদম ফ্রি !!!
আমাদের কাস্টমারদের রিভিউ সমূহ
আলহামদুলিল্লাহ, বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর সেবন করে হাজার হাজার মানুষ উপকার পেয়েছে।
ওয়েবসাইটে অর্ডার করতে সমস্যা হলে যোগাযোগ করুন
ডায়াবেটিসের জন্য ‘বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর’ কেনো ব্যবহার করবেন ?

বিশ্ব-বিখ্যাত মাশরুম বিজ্ঞানী ডাঃ হাবীবুর রহমান তার দীর্ঘ গবেষনার পর প্রস্তুত করেছেন।

মাশ-রুম সহ শতভাগ প্রাকৃতিক উপাদান দিয়ে তৈরি। ফলে এর কোন পার্শ্ব প্রতি-ক্রিয়া নেই ।
অ-গ্নাশ-য়ের উপর জমে থাকা চর্বি কে দ্রু-ত কেটে ফেলে, Ph লেভেলকে ক্ষারীয় করে।
এটা আপনার শরীরে নতুন বিটা-সেল উৎপাদন করে এবং প্রচুর পরিমানে ইন-সুলিন উৎপাদন করে।
ধীরে ধীরে শরীর থেকে ডায়া-বেটিস কে চির বিদায় করে দেয়।

মাত্র ১-২ সপ্তাহের মধ্যে বাজারের ও-ষূধ খাওয়া ছেড়ে দিতে পারবেন।

যারা ইন-সুলিন নেয় তারাও ১-২ মাসের মধ্যে ইন-সুলি-ন ছেড়ে দিতে পারবেন।

শরীরকে পরি-শোধন করে নতুন করে তারু-ন্য ফিরিয়ে আ-নে।
৭-৮ বছর বা আপনার যত পুরাতন ডায়া-বেটিসই হোক না "বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর" সেবনে নিশ্চিত ফলাফল পাবেন ইনশাআল্লাহ
বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর কেন কিনবেন ?
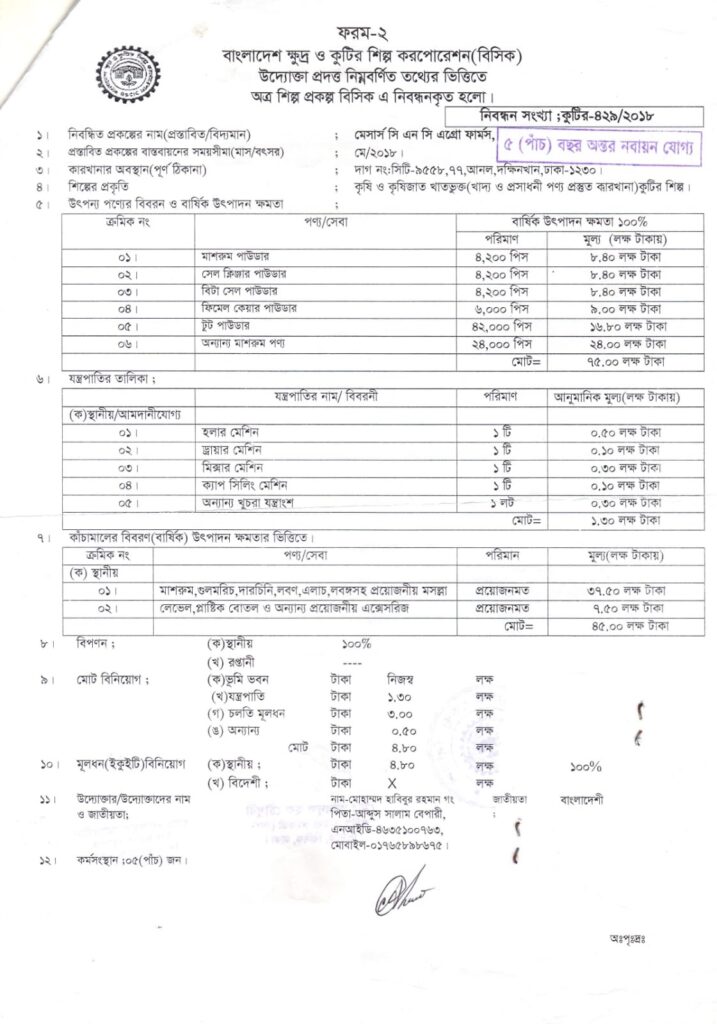
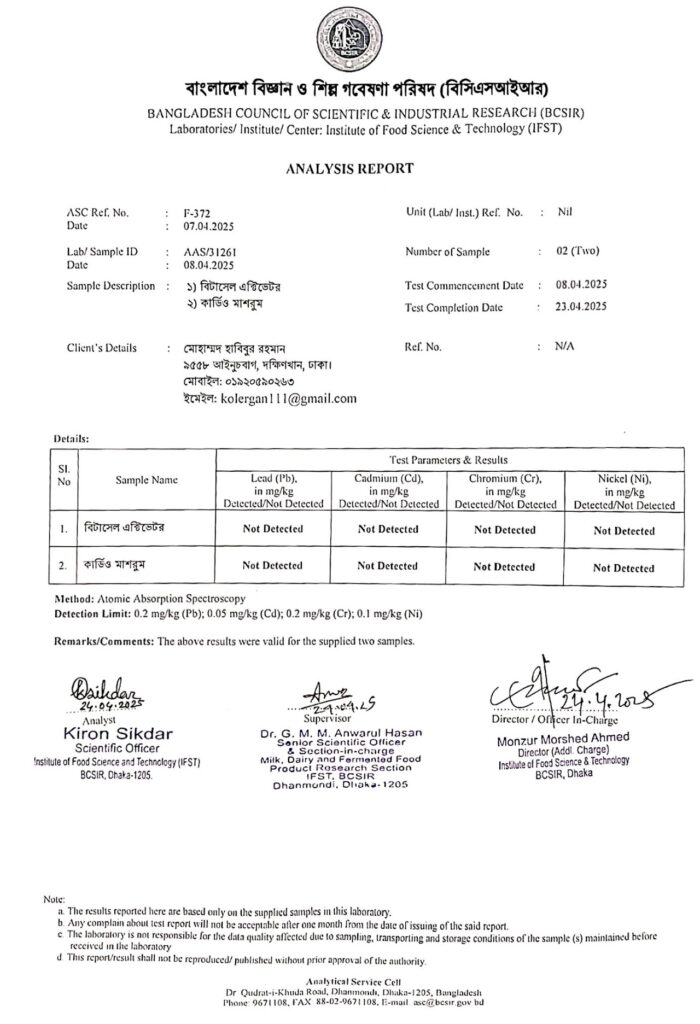
বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর বাংলাদেশ সরকার কর্তৃক অনুমোদিত , ISO Certified ও বিসিক দ্বারা অনুমোদিত একটি Food Suppliment. যা ডায়া-বেটিস এর জন্য শত-ভাগ কার্য-করী ও নিরা-পদ। তাই আপনি নির্ভয়ে সে-বন করতে পারেন।





আমাদের কাছ থেকে কেন কিনবেন ?
- CNC Agro Farm বিটাসেল এক্টিভেটরের প্রস্তুতকারক প্রতিষ্ঠান। মাশরুম কেয়ার বাজারজাতকারী প্রতিষ্ঠান
- আমাদের কোম্পানি সরকার কর্তৃক অনুমোদিত এবং আমাদের ওষুধসমূহ ISO ও বিসিক সার্টিফাইড সহ প্রয়োজনীয় সকল সরকারি অনুমোদনপ্রাপ্ত।
- এটি সম্পূর্ণ হালাল ও প্রাকৃ-তিক উপাদান দ্বারা তৈরি।
- ফলে এর বিন্দুমাত্র পার্শ্ব-প্রতি-ক্রিয়া নেই।
- রাসা-য়নিক কেমিক্যাল মুক্ত সুস্থ জীবন ও মানব সেবাই মূল আমাদের লক্ষ্য।
বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর সেবনের নিয়ম
এক চা চামচ পাউডার আধা গ্লাস পানিতে মিশিয়ে প্রতিদিন সকাল এবং রাতে খাবারের আধা ঘন্টা আগে খেতে হবে।
বিশেষ দ্রষ্টব্য: ১টি জারে ১০০ গ্রাম পাউডার থাকে যা একমাস সেব্য।
বিটা-সেল অ্যাক্টিভেটর মাত্র ০৬ মাস নিয়মিত সেবন করলে আপনি ডায়া-বেটিস থেকে মু-ক্তি পাবেন ইন-শাআল্লাহ। তবে আপনাকে মিষ্টি-জাতীয় খাবার ত্যা-গ করতে হবে এবং অবশ্যই সঠিক নিয়ম মেনে সেবন করতে হবে।
আপনাদের সাধারণ সকল প্রশ্ন ও তার উত্তর (FAQ)
প্রশ্নের উপর ক্লিক করলে উত্তর পেয়ে যাবেন
বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর কি দিয়ে তৈরি ?
বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটরের মূল উপাদান মাশ-রুম এছাড়াও এতে রয়েছে গুরমার, আউবেল, বারবারিন, যষ্টিমধু, কালোজিরা, মেথি সহ আরও ৪১+ প্রাকৃতিক উপাদানসমুহ।
বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর কি ট্যাবলেট নাকি পাউডার ?
বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর একটি পাউডার জাতীয় Food Supplimet.
বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর কি ট্যাবলেট নাকি পাউডার ?
১টি জারে ১০০ গ্রাম পাউডার থাকে যা একমাস সেব্য।
বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর এর কোন সাইড ইফেক্ট আছে কি ?
জি না, বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর শতভাগ প্রাকৃতিক উপাদান দিয়ে তৈরি তাই এর কোন সাইড ইফেক্ট নেই।
বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর কাজ করবে এর গ্যারান্টি কি?
ডঃ হাবিবুর রহমান স্যার তার দীর্ঘ আট বছর গবেষণার পর এই "বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর" তৈরি করেছেন যা সম্পূর্ণ প্রাকৃতিক উপাদান দিয়ে তৈরি। তাছাড়াও এটি বাংলাদেশ সরকার কর্তৃক অনুমোদিত , ISO Certified ও BSTI দ্বারা অনুমোদিত একটি Food Suppliment. যা ডায়া-বেটিস এর জন্য শত-ভাগ কার্যকরী। তাই আপনি নির্ভ-য়ে সেবন করতে পারেন।
কিভাবে সেবন করতে হবে?
এক চা চামচ পাউডার আধা গ্লাস পানিতে মিশিয়ে প্রতিদিন সকাল এবং রাতে খাবারের আধা ঘন্টা আগে খেতে হবে।
কতদিন সেবন করতে হবে?
আপনাকে টোটাল ছয় মাস খেতে হবে। যখন ডায়-বেটিস নিয়ন্ত্রণে চলে আসবে তখন ছেড়ে দিতে পারবেন। তবে আপনাকে মিষ্টি-জাতীয় খাবার ত্যাগ করতে হবে এবং অবশ্যই স-ঠিক নিয়ম মেনে সেবন করতে হবে।
এটি কি সবাই সেবন করতে পারবে?
জি এটি শিশু থেকে বৃদ্ধ সকল বয়সের ডায়া-বেটিসের রোগী সেবন করতে পারবে। তবে যাদের কি-ডনি সি-রাম ক্রি-টিনাইন ২.০০ এর অধিক এবং যে মায়েদের ১-৬ মাসের বাচ্চা আছে, বুকের দুধ খায় এবং গর্ভবতী অবস্থায় সেবন না করা উত্তম।
হা-র্ট ও কিড-নি রোগী কি এটি সেবন করতে পারবে?
জি হা-র্টের রোগী অথবা কি-ডনির রোগী বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর সেবন করতে পারবেন তবে যাদের কিড-নি সিরাম ক্রিটি-নাইন ২.০০ এর অধিক তারা সেবন না করাই উত্তম।
এলো-প্যাথিক ও ইন-সুলিন কি নিতে হবে?
পূর্বের মেডি-সিন ১০ দিন পর্যন্ত চলবে এরপর সু-গার-লেভেল মেপে দেখবে ৬-৭ এর মধ্যে আসলে পূর্বের মেডি-সিন ছেড়ে দিবে। ইনসু-লিন ১৫ দিন একইভাবে নিবে ১৫ দিন পর থেকে ১-২ পয়েন্ট করে কমিয়ে নিয়ে আসতে হবে
পাঁচ থেকে দশ বছরের পুরাতন ডায়া-বেটিস কি ভালো হবে?
জি হ্যাঁ ,আপনার ডায়া-বেটিস যতই পুরাতন হোক না কেন আমাদের বিটা-সেল এক্টিভেটর সেবনে ভালো হবে ইনশা-আল্লাহ । তবে আপনাকে কিছু নিয়ম সেবন করতে হবে।
অর্ডার করতে নিচের ফর্মটি সম্পূর্ণ পূরণ করুন👇
© 2025 Mushroom Care. All Rights Reserved. Designed By CyberBoost Media